Main Actions of Manual Lymph Drainage Techniques
Manual Lymph Drainage Techniques (MLDT) can directly affect the lymphatic system and interstitial fluid and more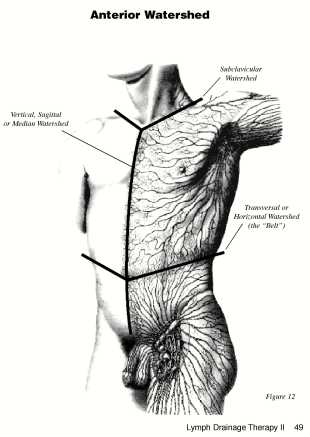 indirectly all body fluids including the venous and arterial blood circulation, as well as the cerebrospinal fluid.
indirectly all body fluids including the venous and arterial blood circulation, as well as the cerebrospinal fluid.
LDT can also affect the immune system, the autonomic nervous system and through techniques like lympho-fascia release (LFR) all the musculoskeletal system, the body framework.
Many benefits can results from these abundant applications. There is a nearly endless list of indications that still need to be explored and scientifically documented.
1- TO ACTIVATE FLUID CIRCULATION
Activation of circulation of lymph, blood capillaries and veins, interstitial liquids, cerebrospinal and synovial fluid, etc..
Applications: help to “reroute” stagnant fluid (edema, primary and secondary lymphedema) in skin, muscles, viscera, joints, cranial sutures, periosteum, chambers of the eyes, cochlea, etc.
2- TO DRAIN
A- TOXINS: As part of treatment to promote tissue regeneration, for example where there are scars, stretch marks, or wrinkles; or where the patient has had a fracture or surgery; some therapists use it for anti-aging applications.
B- FAT: most every time fat content is present in the body lymphatic vessels are present to help evacuate them.
C- MACROMOLECULES (PROTEINS): LDT helps eliminate protein-rich fluid from the extracellular tissue, helping reabsorption of edema.
3- TO STIMULATE THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Increased lymph flow carries more antigens to the lymph nodes, increasing antibody/antigen contact. This can help the immune system in the following ways:
LDT can be utilized for preventative action.
Lymphatic drainage techniques have been found to help with chronic and subacute inflammatory processes, e.g. chronic fatigue syndrome, auto-immune disease, arthritis, bronchitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, acne, eczema, etc
4- TO STIMULATE THE PARASYMPATHETIC SYSTEM
Stimulation of the lymphatics tends to increase parasympathetic and diminish sympathetic tone, the “fight or flight” response. This can be very helpful in dealing with:
Stress, depression or sleeping disorders
5- TO REDUCE PAIN
LDT alleviates tissue fluid stagnation and inhibits type C nociceptors which trigger pain (Foldi, Alois, Brugger). It is effective in dealing with some kinds of chronic pain.
6- TO REDUCE MUSCLE SPASM
Skeletal or smooth muscle spasms, constipation, etc.
Possible Indications for Lymph Drainage Therapy (LDT)
The following are ailments that responded favorably in therapists’ clinics. All the necessary studies have not yet been done, nor have all applications of Lymph Drainage Therapy been discovered.
The following pathologies are only reference points for those who do not have experience with lymph drainage. Every case has to be considered individually. All contraindications learned in class are to be carefully respected.
1- Angiology - Cardiology - Lymphology:
Edema is abnormal accumulation of fluid in the extracellular compartment. Not all edemas are good indications for LDT and all will not respond in the same manner.
- Lymphedema or lymphostatic (high protein) edema: in these cases, the lymphatic system itself is not functioning properly. This is a mechanical insufficiency. Lymphostatic edema is one of the principal medical indications for lymphatic drainage, in combination with other modalities.
- Lymphodynamic edemas: by contrast these are conditions in which the lymph vessels are still functioning properly but they cannot remove the excessive accumulation of fluid in the connective tissue. They do not respond as well to manual therapy.
Edemas of different origins may include:
- Traumatic: strained muscles, sprained ligaments, joint dislocations, tendinitis, tenosynovitis, fracture (before, during, after being in a cast), hematomas, “ski thumb” injury, etc.The reduction of the edema makes possible earlier, less painful mobilization, and prepares the tissue before applying the plaster.
- Post-infectious (dental, ENT, etc.)
- Dermatologic: chronic eczema, etc.
- Pediatric
- Premenstrual, cyclic-idiopathic
- Gynecologic
- Neurologic: for neuralgia, facial paresis, multiple sclerosis, etc.
- Edemas associated with rheumatism or autoimmune diseases (e.g., arthrosis, polyarthric problems)
- Nephrologic (nephrotic)
- Lipolymphedema
- Edemas of venolymphatic origin
Nearly all conditions may be drained: from the early stages of venous disease to varicose veins, post-thrombotic leg edemas and hypodermitis, and even late chronic complications such as venous ulcer. Always keep in mind, however, the absolute contraindication of acute phlebitis.
- Arteritic ulcer, and other types of ulcers (e.g. diabetes mellitus ulcer)
- Arterial hypertension
- Arteritis, intermittent claudication (intermittent limping)
- Raynaud’s disease
2- Dentistry, Orthodontics:
- Tooth pain
- Post- extraction pain, edema, inflammation, hematoma, scarring, etc.
- Orthodontia, root canal, orthodontic surgery
- Gingivopathy (gum disease), periodontitis
3- Dermatology (Skin):
- Acne vulgaris
- Rosacea
- Seborrhea
- Chronic and allergic eczema: avoid the area in the early stage to prevent inflammatory or allergic reactions.
- Perioral dermatitis (from cortisone treatments)
- Certain pigmentation spots
4- Esthetic:
- Skin complexion
- Erythrosis (telangiectasia or couperose)
- Tissue ptosis
- Wrinkles
- Adiposis, cellulite
5- General / Metabolic:
- Stress
- Fatigue
- Chronic pain
- Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), Epstein-Barr virus.A very common disorder, not yet well understood.
- Autonomic dystonia
- Sleeping disorders
- Snoring
- Detoxification: fasting, dieting, tobacco withdrawal, withdrawal from other substance dependency.
- Toxic chemical poisoning
- Jet lag
- Alcohol hangover
- Metabolic effects on cholesterol, uric acid, etc.
6- Gerontology / Geriatric:
LDT is a good technique to use with elderly people because of its profound efficacy in promoting tissue regeneration and oxygenation and deep cleansing of the body. It also has a stimulating effect on the immune system and is effective in relieving stress, and helping with general health maintenance.
If the contraindications are carefully respected, LDT can be applied to almost every indication with elderly patients because of its gentleness and harmlessness. LDT can be used at home on family members. The patient/clients reaction needs to be monitored in the first three or four treatments by treating for shorter sessions and evaluating.
Cerebral degeneration and memory loss may benefit from LDT.
7- Gynecology:
- Menstruation: PMS, painful or hemorrhagic menses- Breast pain or swollen breasts (from menses, birth control pill, pregnancy)
- Pregnancy: Stretch marks (abdomen, breasts): “striae gravidarum,” “cutis striata lymphostatica.” The results are better if the drainage is started in the early stages.
- Edematous legs
- Breast feeding: breast soreness, cracks or fissures in the puerperal period, prevention or treatment of scarring, prevention of infection.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy (ANDI: Aberrations of normal development or involution)
- Infertility
8- Hepato-Gastroenterology:
- Chronic constipation
- Chronic gastritis, gastroenteritis, stress ulcers, enterocolitis, chronic colitis
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Chronic ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease
- Diverticulosis, diverticulitis,
- Chronic appendicitis
- Chronic pancreatic insufficiency, chronic pancreatitis
- Malabsorption, celiac disease
- Hemorrhoids, anal fissure
- Chronic hepatitis
- Chronic cholecystitis, cholangitis
- Food poisoning
9- Infectious Diseases: (Also Check Dermatology, General, Ophthalmology, Pneumonology):
You can use it with pediatric clients (children) or geriatric patients (elderly people). Take care to do short sessions initially to avoid inflammatory reactions.
- Chronic pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, rhinitis, otitis, syringitis
- Chronic sinusitis
- HIV, AIDS: Be very careful; check with a physician. The reactions may differ depending on the stage of the disease.
10- Neurology:
- Headache, migraine
- Post trauma symptoms (headaches, vertigo)
- Cerebrovascular accident (stroke), hemiplegia, chronic ischemic syndrome, various encephalopathies
- Concussion (commotio cerebri, commotio spinalis)
- Spinal injuries
- Cerebral palsy (Little’s disease)
- Facial neuralgia, intercostal neuralgia, herpes zoster neuralgia, etc.
- Facial paralysis
- Parkinson’s disease (rare diminution of the tremor)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): crisis times may become shorter and the remission periods of MS longer with lymph drainage.
- Vertigo
- Peripheral nerve disorders / cranial nerve disorders (facial nerve paralysis, trigeminal neuralgia, Bell’s palsy)
- Myopathy, muscular dystrophy or atrophy
- Spinal poliomyelitis (effective with resultant edemas)
- Epilepsy
11- Ophthalmology:
- Visual acuity
- Scotoma
- Chronic dacryocystitis (infection of the lachrymal sac), blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid margins)
- Chronic glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Chronic edema of the eyelids
- Macular degeneration
- Retinitis pigmentosa
12- Orthopedics (Bones-Tendons-Surgery):
- Trauma
- Hematoma
- Sprain
- Dislocation, subluxation
- Ligament and meniscus pathologies
- Fracture
- Post-fracture or post-sprain symptoms (pain, discomfort, etc.)
- Neck pain, whiplash
13- Otorhinolaryngology - ORL (Ear-Nose-Throat):
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
- Vertigo
- Hearing loss, otosclerosis
- Meniere’s disease
- Labyrinthitis
- Asialia - Hyposalivation
- Sjogren’s syndrome (Dry eyes and mouth)
14- Pediatrics:
LDT can be applied to children for all diseases listed. However, be especially careful not to aggravate high fever in a child.
15- Pneumonology, Allergology:
- Chronic bronchitis, emphysematous bronchitis
- Bronchial asthma:
- Emphysema
- Post-pleuritic disorders
- Silicosis: pneumoconiosis resulting from inhalation of silica (quartz) dust
- Cystic fibrosis (mucoviscidosis)
- Hay fever
16- Rheumatology: Disorders of Bone/Articulations, Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue
Lymph drainage can effectively alleviate the edemas of many rheumatologic ailments after signs of acute inflammation have disappeared.
- Arthrosis (neck, shoulders, hips, knees)
- Rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, polyarthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Gout, chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout)
- Psoriatic arthritis (arthritis associated with psoriasis)
- Allergic arthropathy, endocrine arthropathy, diabetic arthropathy, etc.
- Lupus erythematosus
- Scleroderma: LDT yields especially good effects on the sclerotic skin of hands and face.
- Fibromyalgia syndrome
- Osteoporosis
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome (RSDS)
- Fibrositis syndrome (bursitis, tendinitis, tenosynovitis, tenoperiostosis, etc.)
- Myositis, myofibrositis, polymyositis and dermatomyositis
- Tennis elbow (lateral humeral epicondylitis), golfer elbow (medial humeral epicondylitis)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Dupuytren’s contracture
- Spasmodic torticollis
- Nocturnal paresthetic brachialgia
17- Sports Medicine:
- Sport preparation: to improve the condition of muscles before and after a sporting event
- Muscle spasms
- Sports trauma: edemas, hematoma (be sure that any bleeding has stopped).
- Traumatic edemas: torn muscles, sprained articulations and ligaments, joint dislocations, edemas after meniscus and ligament lesions, tendinitis, tenosynovitis, fracture (before/during/after cast), hematomas, "ski thumb" injuries, etc. The reduction of the edema allows for earlier, less painful mobilization, and can prepare the tissue before applying the plaster.
- Sprains, dislocations, etc.
- Muscle cramps or pain
- Ligamentous and meniscal lesions
- Fractures (in or out of cast)
- Scars / Fibrosis
18-Surgery:
- Pre-surgery: prepares the tissue for the intervention, drains the tissue, clears the lymph passages to help prevent post-surgery edema.
- Post-surgery
- Reduction or prevention of scars and fibrosis, has antalgic and infection-preventing effects, and also has some effectiveness in reducing the formation of hypertrophic scars or “keloids”.
- For surgery involving the removal of lymph nodes (post-mastectomy, post-prostatectomy, post-hysterectomy, post-ovariectomy, post-nephrectomy, ORL surgery, tumor removal)
- Limb amputation
- Skin grafts, burns and their surgical treatment
19- Urology, Nephrology (Bladder, Kidneys):
All pathologies with the frequent chronic pain, edema, inflammation.
20- Veterinary:
Lymph drainage can be applied to many domesticated animals, including dogs, cats, horses, cows, pigs and sheep.